Earthquakes
One exciting thing from earthquake is the study of seismic waves leading to the discovery of outer core layer being liquid.
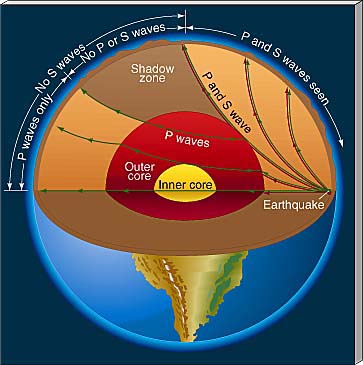
One exciting thing from earthquake is the study of seismic waves leading to the discovery of outer core layer being liquid.

| Word | Definition |
|---|---|
| Primary waves | are P-waves. fastest. longitudinal = vibrates back and forth |
| Secondary waves | are S-waves. slower. transverse = vibrates from side to side. |
| Earthquake | sudden movement of Earth's crust that releases energy. |
| Focus | is the origin of an earthquake. |
| Epicenter | is the place directly above the focus on Earth's surface. |
| Refraction | P-waves change direction as it enters into a different layer. |
| Seismograph | a machine that records the earthquake waves. |
| Seismogram | a recording of earthquake waves. |
| Origin time | the time when both P-wave and S-wave start to travel. |
| Travel time | the time for earthquake waves to travel. |
| Subduction | Two tectonic plates converge. One plate goes underneath another plate. |
| Seafloor spreading | happens at the mid-ocean ridge where new magma comes out as 2 plates diverge. |
Alternating parallel bands of normal and reversed
magnetic polarity are found in the basaltic
bedrock on either side of the
(1) Mid-Atlantic Ridge
(2) Yellowstone Hot Spot
(3) San Andreas Fault
(4) Peru-Chile Trench